India, one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing economies, has faced significant challenges in recent years that have impacted its economic landscape https://finanzasdomesticas.com/economia-de-india-afectada/. This article provides essential information on how India’s economy has been affected, exploring the key challenges, impacts, and measures being taken for recovery.
Introduction To https://finanzasdomesticas.com/economia-de-india-afectada/
India’s economy is a dynamic and complex system influenced by a variety of factors, including domestic policies, global events, and socio-economic conditions. Understanding the recent challenges and their implications is crucial for comprehending the current state and future prospects of India’s economic health.
Key Challenges Facing India’s Economy
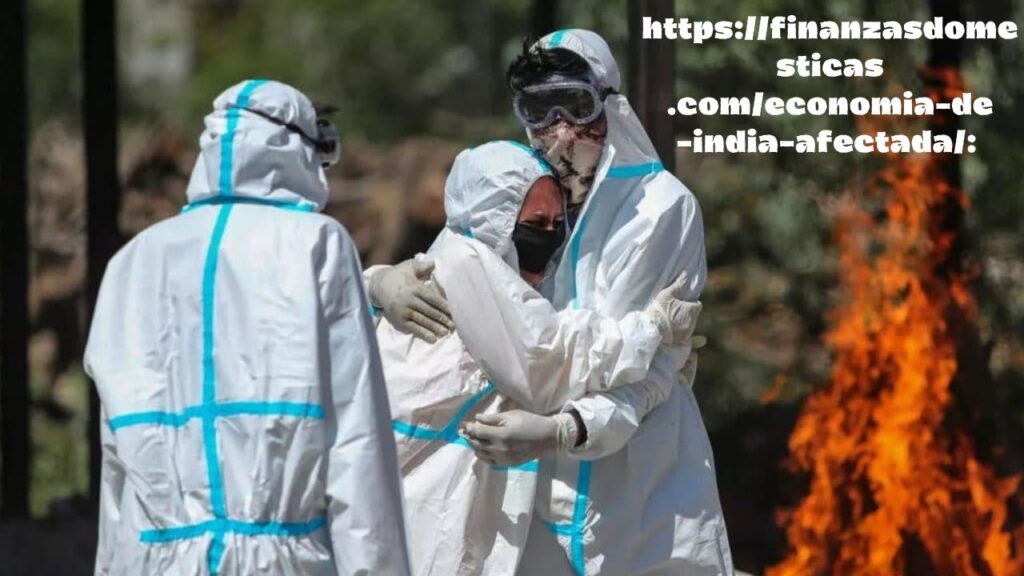
COVID-19 Pandemic
Overview: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on India’s economy, causing disruptions across various sectors.
Impacts:
- Lockdowns and Restrictions: Repeated lockdowns and restrictions severely affected businesses, leading to closures and reduced economic activity.
- Unemployment: Millions of people lost their jobs, particularly in the informal sector, which constitutes a significant portion of India’s workforce.
- Healthcare Strain: The healthcare system faced unprecedented pressure, affecting the overall productivity and economic stability.
Measures for Recovery:
- Vaccination Drive: A massive vaccination campaign aimed at controlling the spread of the virus and restoring normalcy.
- Economic Stimulus: The government introduced several stimulus packages to support businesses, provide financial aid, and boost economic recovery.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Overview: Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the pandemic, impacted various industries in India, from manufacturing to services https://finanzasdomesticas.com/economia-de-india-afectada/.
Impacts:
- Production Delays: Shortages of raw materials and components led to production delays in key industries like automotive and electronics.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in prices of essential goods and commodities affected both consumers and businesses.
- Trade Imbalances: Disruptions in international trade affected exports and imports, leading to trade imbalances.
Measures for Recovery:
- Domestic Production Incentives: Programs like ‘Make in India’ aimed to boost local manufacturing and reduce dependency on imports.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Initiatives to diversify supply chains and improve logistical infrastructure to enhance resilience.
Agricultural Challenges
Overview: Agriculture, a critical sector in India’s economy, faced several challenges, including policy reforms, climate change, and market disruptions.
Impacts:
- Farmers’ Protests: Policy reforms, particularly the new farm laws, led to widespread protests and uncertainty in the agricultural sector.
- Climate Change: Erratic weather patterns and natural disasters affected crop yields and agricultural productivity.
- Market Access: Farmers struggled with access to markets, fair pricing, and infrastructure, impacting their incomes and livelihoods.
Measures for Recovery:
- Policy Revisions: The government engaged in dialogue with farmers to address concerns and revise contentious policies.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Promoting sustainable and climate-resilient agricultural practices to mitigate the impact of climate change.
- Market Reforms: Improving market access and infrastructure to ensure fair pricing and better income for farmers.
Also Read: https://notipostingt.com/2022/04/27/que-se-necesita-para-viajar-a-qatar/: In-Depth Analysis
Economic Impacts
GDP Growth Slowdown
Overview: India’s GDP growth rate slowed significantly due to the combined effects of the pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and other economic challenges.
Impacts:
- Contraction: The economy experienced a contraction, with GDP shrinking in some quarters.
- Investment Decline: Reduced investor confidence led to a decline in domestic and foreign investments.
- Consumption Drop: Consumer spending, a key driver of GDP, decreased due to income losses and economic uncertainty.
Measures for Recovery:
- Economic Reforms: Structural reforms aimed at boosting investment, enhancing productivity, and stimulating growth.
- Monetary Policies: The Reserve Bank of India implemented accommodative monetary policies to support economic recovery.
- Fiscal Stimulus: Increased government spending on infrastructure and social programs to spur economic activity.
Inflation and Cost of Living
Overview: Inflation rates fluctuated, impacting the cost of living and purchasing power of consumers.
Impacts:
- Price Increases: Prices of essential goods, including food and fuel, increased, affecting household budgets.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Higher costs of living reduced the purchasing power of consumers, impacting overall demand.
- Income Disparities: Inflation disproportionately affected lower-income households, exacerbating economic inequalities.
Measures for Recovery:
- Price Controls: The government implemented measures to control prices of essential commodities and stabilize inflation.
- Subsidies: Providing subsidies and financial aid to vulnerable populations to mitigate the impact of inflation.
- Monetary Policy Adjustments: The central bank adjusted interest rates and other monetary tools to manage inflation.
Sector-Specific Impacts
Manufacturing and Industry
Overview: The manufacturing sector, a vital component of India’s economy, faced significant disruptions due to the pandemic and supply chain issues.
Impacts:
- Production Halts: Lockdowns and supply chain disruptions led to temporary halts in production.
- Labor Shortages: Migrant labor shortages affected manufacturing activities, particularly in labor-intensive industries.
- Export Challenges: Declines in global demand and logistical challenges impacted exports.
Measures for Recovery:
- Incentive Programs: Initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aimed to boost manufacturing output and exports.
- Skill Development: Programs to reskill and upskill the workforce to meet the demands of the manufacturing sector.
- Export Promotion: Efforts to enhance export competitiveness and access to international markets.
Services Sector
Overview: The services sector, including IT, tourism, and hospitality, was heavily impacted by travel restrictions and reduced consumer spending.
Impacts:
- Tourism Decline: Travel bans and lockdowns led to a sharp decline in tourism, affecting hotels, restaurants, and related businesses.
- IT and Remote Work: The IT sector adapted to remote work, but faced challenges in project execution and client engagement.
- Financial Services: The banking and financial services sector dealt with increased loan defaults and reduced profitability.
Measures for Recovery:
- Tourism Support: Initiatives to promote domestic tourism and provide financial support to the hospitality sector.
- Digital Transformation: Accelerating digital adoption in the IT sector to enhance remote work capabilities and service delivery.
- Financial Stability: Measures to strengthen financial institutions and provide liquidity support to businesses.
Recovery and Future Prospects
Economic Reforms and Policies
Overview: The Indian government has introduced several economic reforms and policies to foster recovery and ensure long-term growth.
Key Initiatives:
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: A self-reliant India campaign aimed at boosting domestic production, innovation, and economic resilience.
- Infrastructure Development: Significant investments in infrastructure projects to spur economic growth and create jobs.
- Ease of Doing Business: Reforms to improve the business environment, attract investments, and enhance regulatory frameworks.
Sustainable Growth
Overview: Emphasizing sustainable growth to ensure long-term economic stability and environmental sustainability.
Key Areas:
- Green Energy: Promoting renewable energy sources and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Encouraging sustainable farming practices and ensuring food security.
- Climate Action: Implementing policies to address climate change and mitigate its economic impact.
Also Read: https://notipostingt.com/2022/04/27/que-ver-y-hacer-en-isla-de-gozo : Full Details
Conclusion
India’s economy has faced significant challenges in recent years, driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions, agricultural issues, and more https://finanzasdomesticas.com/economia-de-india-afectada/. However, with strategic measures and reforms, India is poised for recovery and sustainable growth. Understanding these challenges and the steps taken to address them provides valuable insights into the resilience and potential of India’s economic landscape.
FAQs
What were the major challenges affecting India’s economy in recent years?
Major challenges included the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions, agricultural issues, and economic slowdown.
How did the COVID-19 pandemic impact India’s economy?
The pandemic led to lockdowns, job losses, business closures, and healthcare strain, significantly impacting economic activity.
What measures have been taken to support economic recovery in India?
Measures include vaccination drives, economic stimulus packages, monetary policies, and structural reforms aimed at boosting growth and resilience.
How has the agricultural sector been affected in India?
The agricultural sector faced challenges such as policy reforms, climate change, and market disruptions, impacting farmers’ incomes and productivity.
What are the future prospects for India’s economy?
With continued reforms, infrastructure development, and emphasis on sustainable growth, India’s economy is poised for recovery and long-term stability.